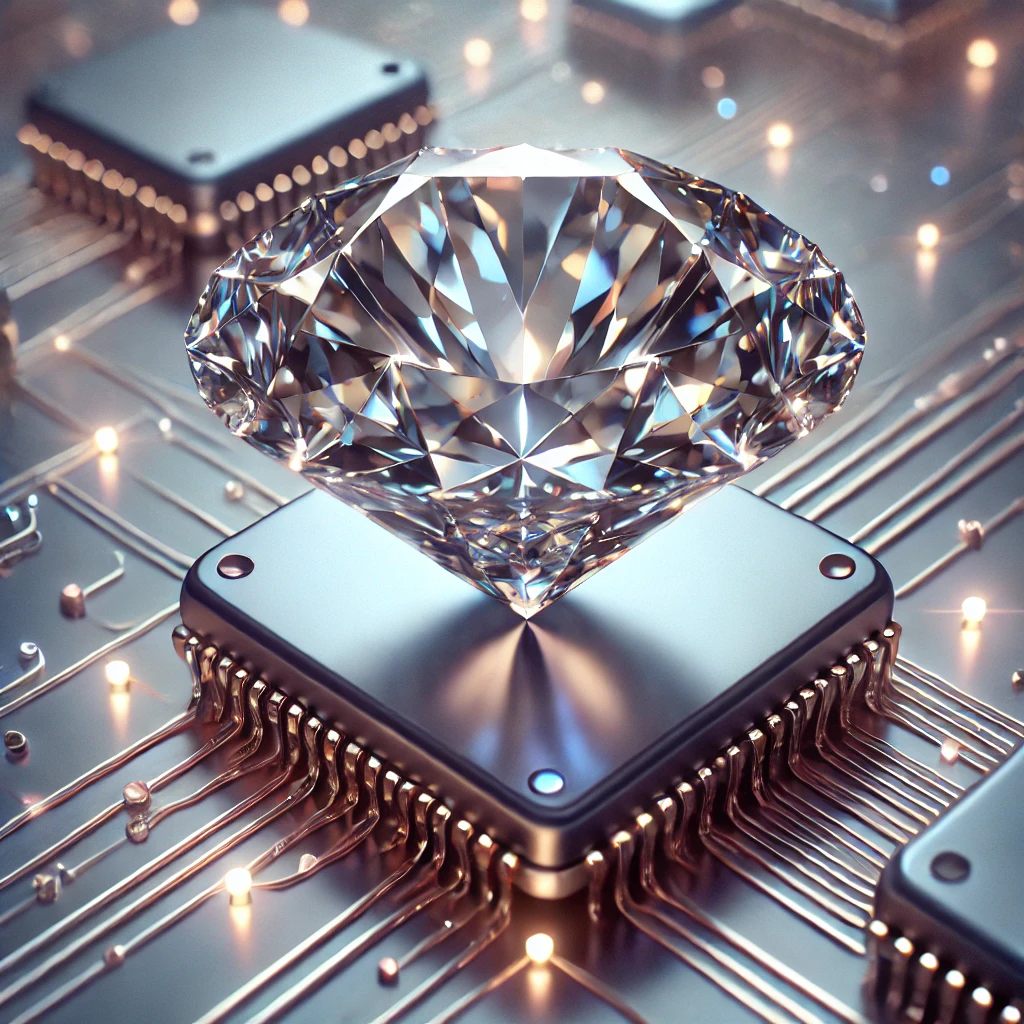
A diamond can do both! Even though they have become famous for their symbol of luxury and beauty, their use extends far beyond the traditional role in the jewellery industry. Diamonds have been recently unvalued as key players in quantum computing, semiconductors, electronics, and optical applications. Understanding diamond’s extraordinary properties can unlock their full potential, revolutionising industries and further developing technology.
In this article, we will primarily focus on quantum computing which is seen as the “next big thing”. Despite the continuous progress, the current field is not fully mature yet.
Diamonds in Quantum Computing: Revealing New Possibilities
Firstly, what is quantum computing? While it is composed of many disciplines, quant computing takes advantage of quantum physics to operate faster and better than conventional computing.
Diamonds, specifically those containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres, can be utilised as qubits which are the fundamental units of quantum information aka the building blocks of quantum computers. There has been a lot of recent research at MIT and MITRE with researchers using diamond colour centres as qubits due to their scalability and compatibility with modern semiconductor manufacturing. These colour centers are compact meaning they have longer stability and can be manipulated at room temperature. (Fun fact: Most quantum systems are kept inside very very cold refrigerators!)
Beyond computing, these NV centres in diamonds can also be used to develop quantum sensors to detect minute changes in magnetic fields. This is highly valuable in the scientific field.
Diamonds as Semiconductors: Advancing Electronics
Among all the unique properties of diamonds, there are 2, thermal conductivity and wide bandgap, that make them ideal as semiconductors in electronics. They can handle very high voltages and temperatures which is essential for high-power electronics. This can be used in renewable energy systems, contributing to sustainable technology solutions. Diamonds’ superior heat dissipation properties limit overheating problems and are still efficient in their performance.
But these are just 2 examples! Diamonds have many more properties and abilities that make them valuable in a variety of high-tech applications.
- Radiation-Hardened Electronics: Diamonds have resistance to radiation and are therefore being used to create radiation-hardened electronics
- Optical Applications: Having a very broad transmission spectrum, diamonds have found their use in spectroscopy and the development of advanced lenses and coatings.
Are There Any Challenges?
- Synthetic diamonds are mainly used for all these technological applications, which means they must be scaled up to meet demand in the future.
- Diamond-based technologies are very expensive!
- Not all technology is fully developed yet
Conclusion
The future of diamonds extends far beyond their traditional role in the jewellery industry.
With the variety and amount of properties diamonds have, they can outperform many materials that are currently being used in technology and the growth of synthetic diamonds will have a great impact in the engineering world. Despite the challenges that the industry is currently facing, the opportunities are incredibly promising! In fact, this is only the beginning, and their potential can revolutionise the world!